Circular Flow of Income: Class 12 Economics CBSE (2025-26 Edition)
The Ultimate Guide for Students & Professionals
📋 Description
Take your Economics learning to the next level! This comprehensive guide on the circular flow of income breaks down complex concepts into easy, actionable steps—perfect for Class 12 CBSE students, curious beginners, or professionals revisiting the basics. Explore high-scoring diagrams, relatable examples, trending keywords, SEO-rich insights, and interactive tips. Learn how money, goods, and services move in a never-ending loop and why it matters for you, India, and the world.
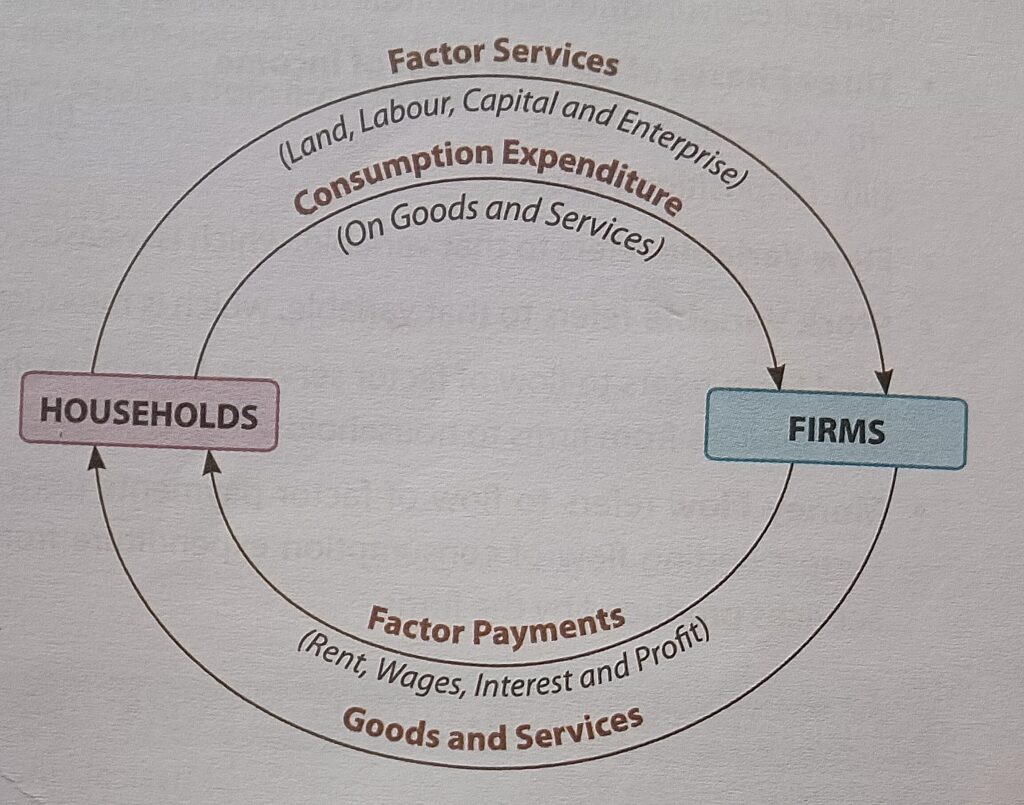
1. What is the Circular Flow of Income? [Keyword: Circular Flow of Income Class 12 Economics]
The circular flow of income is a concept showing how money, goods, and services circulate seamlessly through an economy. Basically, it tracks the way people earn, spend, and recycle money—creating a continuous, closed loop123.
In simple terms: what you spend comes back as someone else’s income and vice versa.
Key Points:
- Explains how money moves between households and firms.
- Reveals the invisible connections in every modern economy.
- Shows that income, spending, and production are interconnected.
2. Why Is It Important? [Keywords: Importance, Benefits, Class 12 Economics]
Understanding the circular flow…
- Builds strong exam answers and improves analytical skills.
- Prepares you for real-world economics (budgeting, investments, business).
- Helps you see the link between your spending and the larger economy.
- Essential for scoring high in CBSE exams and competitive tests.
- Makes complex ideas like national income and GDP much easier to grasp142.
3. Main Sectors: Who Are the Players? [Keywords: Households, Firms, Sectors]
The classic model features two core sectors:
Households:
- Provide factors of production (land, labor, capital, entrepreneurship).
- Spend income on goods/services.
Firms (Businesses):
- Produce goods/services.
- Pay households as wages, rent, interest, and profits.
In more detailed models: Government and Foreign Sector also join the circle356.
Circular Flow of Income: Class 12 Economics CBSE
4. The Two-Sector Model Explained [Primary SEO Phrase: Two-Sector Model Circular Flow]
The two-sector model is like the ABCs of the circular flow. It’s simple, powerful, and perfect for scoring full marks in CBSE Class 1223:
SectorMain FunctionHouseholdsSupply resources; spend on goods/servicesFirmsProduce goods/services; pay incomes
- No savings: Every rupee earned is spent.
- Closed economy: No government or foreign trade.
Bonus: This model helps you master later, more complex models with ease.
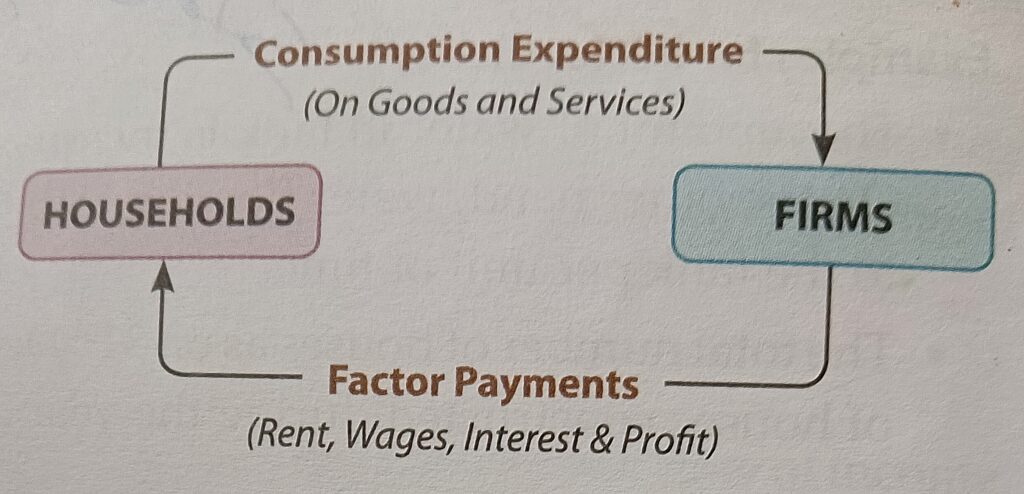
5. Real Flow vs. Money Flow [Keywords: Real Flow, Money Flow, Diagrams]
Real Flow: Movement of goods/services from firms to households and resources from households to firms.
Money Flow: The movement of money—households receive income and spend it on goods/services from firms.
Flow TypeExampleReal FlowWheat sent from a farm to a bakeryMoney FlowBakery pays wages; you buy bread
Remember: Both flows are continuous and happen at the same time, maintaining a balanced economy123.
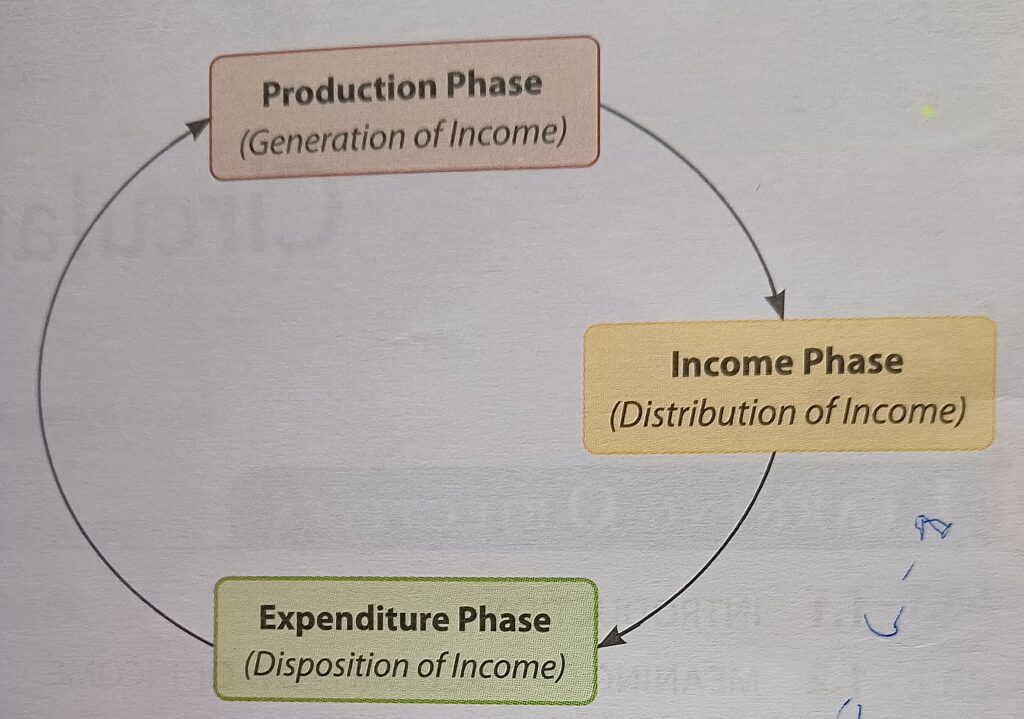
6. Three Phases of the Circular Flow
These phases ensure the economy keeps moving:
- Generation Phase: Firms produce goods/services using household resources.
- Distribution Phase: Firms pay households (wages, rent, interest, profit).
- Disposition Phase: Households spend their income on goods/services from firms12.
7. Step-by-Step Process with Infographic
How the Circular Flow Works in Daily Life:
- You go to work (supply labor).
- You earn a salary (income).
- You buy groceries (spending).
- The grocery store owner earns money and pays staff.
- Staff buys other goods… The cycle never ends!
- Households → Resources → Firms
- Firms → Goods/Services → Households
- Inner arrow: Money flow (wages, rent, interest, profit)
- Outer arrow: Goods/services and resources
(Circular Flow of Income: Class 12 Economics CBSE)
8. Real-Life Example Anyone Can Relate To
Imagine you work at a bakery. Here’s the flow:
- You (household) work and earn a wage.
- You spend part of your wage on buying a loaf of bread from the same bakery.
- The bakery (firm) uses your payment to buy more flour and pay other workers.
- The miller gets paid and spends on other things, continuing the cycle7.
This loop is what keeps everyone in business and ensures you can buy what you need.
9. Advanced Perspectives: More Than Two Sectors [Keywords: Open Economy Model, Government Sector, Foreign Sector]
In reality, economies involve other sectors:
- Government: Taxes and spends on welfare, infrastructure, etc.
- Foreign Sector: Imports and exports add international flows.
These add complexity but follow the same circular logic—just with more arrows and more players!256.
Circular Flow of Income: Class 12 Economics CBSE
10. Common Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What if people save part of their income?
A: Savings are considered “leakages”—they leave the loop temporarily, but can return via investments.
Q2: How is the circular flow model used in exams?
A: Draw neat diagrams, label flows clearly, mention phases, and give simple examples. Always link back to real life or current events for extra marks.
11. Actionable Checklist for Students
- Always draw the circular flow diagram in related questions!
- Use keywords like “real flow,” “money flow,” “two-sector economy.”
- Remember: Production = Income = Expenditure in the model.
- Relate examples to daily life (shops, salaries, businesses).
12. Key Takeaways & Conclusion 🏁
- Circular flow of income shows how money, goods, and services move continuously.
- The model explains why income always equals production and spending in a simple economy.
- It teaches us how businesses, workers, and consumers depend on each other.
- The core principles apply to every modern economy—even with governments and foreign trade involved.
Master this concept—and you master the “heartbeat” of economics!
13. Inspirational Closing & Next Steps 🌟
“Every rupee you spend circulates, creating value—not just for you, but for the whole economy.”
Circular Flow of Income: Class 12 Economics CBSE
14. Actionable Call-to-Action 👉
- Download this post as a handy PDF revision guide!
- Try a real-world challenge: Track your next five purchases and think about how your money keeps the economy moving.
- Share this post with classmates or friends to help them succeed.
- Explore more: Check out related posts on national income, GDP, and open economy models.
- Quiz Yourself:
- What are the two main sectors in the simple circular flow?
- What does “money flow” represent?
- How does savings affect the flow?
- Poll:
- Have you ever thought about where your salary/spending ends up?
- Downloadable:
Related Resources & Indian Authority Links
Keep learning, keep exploring—and remember, your understanding of the circular flow is your ticket to exam success and financial awareness!
Circular Flow of Income: Class 12 Economics CBSE