National Income and Related Aggregates – Class 12 Economics
Understanding national income is an important part of macroeconomics. It helps us know how much wealth a country produces in a year. This article covers the basic aggregates of national income, their definitions, formulas, and differences, written in simple language for class 12 students.
What is National Income?
National Income means the total monetary worth of all final goods and services produced within a country during a financial year. Because goods and services are very different (like thousands of wheat or mobile phones), their quantities cannot be added, so we use money value to combine and add them together.
National Income and Related Aggregates
Basic Aggregates of National Income
There are eight main aggregates or measures in national income accounting:
- Gross Domestic Product at Market Price (GDPMP)
- Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost (GDPFC)
- Net Domestic Product at Market Price (NDPMP)
- Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost (NDPFC or income earned within the country)
- Gross National Product at Market Price (GNPMP)
- Gross National Product at Factor Cost (GNPFC)
- Net National Product at Market Price (NNPMP)
- Net National Product at Factor Cost (NNPFC or income earned by residents of the country)
Explanation of Key Aggregates
1. Gross Domestic Product at Market Price (GDPMP)
- Definition: Money value of all final goods and services produced within the domestic territory of a country (by all producers) in one year at market prices.
- Includes: Indirect taxes, excludes subsidies, includes depreciation.
- Formula: No adjustment; this is the base value.
2. Gross Domestic Product at Factor Cost (GDPFC)
- Definition: GDP calculated at the cost paid to factors of production (like wages, rent, etc.), excluding net indirect taxes.
- Formula:
GDPFC = GDPMP − Net Indirect Taxes
Net Indirect Taxes = Indirect Taxes − Subsidies
3. Net Domestic Product at Market Price (NDPMP)
- Definition: GDPMP minus depreciation (value reduction in asset over time because of regular usage and wear).
- Formula:
NDPMP = GDPMP − Depreciation
4. Net Domestic Product at Factor Cost (NDPFC)
- Definition: Final goods/services produced within domestic territory after excluding depreciation and indirect taxes.
- Formula:
NDPFC = GDPMP − Net Indirect Taxes − Depreciation - Also called: income earned within the country
5. Gross National Product at Market Price (GNPMP)
- Definition: GDPMP plus Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA, i.e., income from abroad minus payments to abroad).
- Formula:
GNPMP = GDPMP + Net Factor Income from Abroad
6. Gross National Product at Factor Cost (GNPFC)
- Formula:
GNPFC = GNPMP − Net Indirect Taxes
7. Net National Product at Market Price (NNPMP)
- Formula:
NNPMP = GNPMP − Depreciation
8. Net National Product at Factor Cost (NNPFC)
- Definition: Value of all final goods and services produced by normal residents of a country in one year (includes NFIA, excludes depreciation and indirect taxes).
- Formula:
NNPFC = GNPMP − Net Indirect Taxes − Depreciation - Also called: income earned by residents of the country
How to Convert Between Aggregates
You can convert one aggregate into another by following these four adjustment steps:
- Add or subtract Depreciation (to go between Gross and Net measures)
- Add or subtract Net Indirect Taxes (to go between Market Price and Factor Cost)
- Add or subtract Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA) (to go between Domestic and National concepts)
Flow Diagram: Relationship between Domestic and National Aggregates
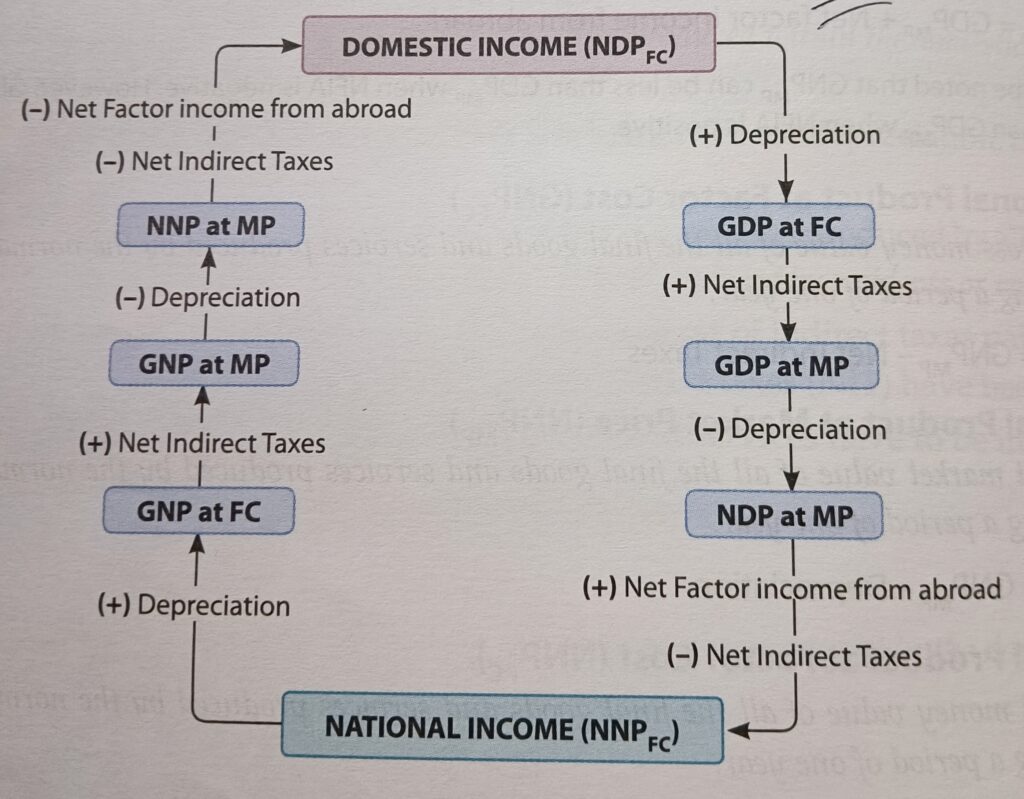
Key Differences
Domestic Income (NDPFC) vs National Income (NNPFC)
| Basis | Domestic Income (NDPFC) | National Income (NNPFC) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature of Concept | Territorial – only inside country’s border | Nationality – includes income of residents worldwide |
| Category of Producers | All producers in the country | Only normal residents (may be outside country too) |
| Includes NFIA? | No | Yes |
| Also Called | Domestic Factor Income | National Income |
GDPMP vs National Income (NNPFC)
| Basis | GDPMP (Gross Domestic Product at Market Price) | National Income (NNPFC) |
|---|---|---|
| Nature | Territorial (domestic territory) | National (by residents only) |
| Producers Included | All producers in domestic territory | Normal residents, even if abroad |
| Net Indirect Taxes | Included | Excluded |
| Depreciation | Included | Excluded |
Simple Explanation of Terms
- Gross: Before removing depreciation.
- Net: After removing depreciation.
- Domestic: Inside country’s territory.
- National: By normal residents (includes income from abroad).
- At Market Price: Includes net indirect taxes.
- At Factor Cost: Excludes net indirect taxes.
- Net Indirect Taxes: Indirect taxes minus subsidies.
- Depreciation: Loss in value of assets over time.
- Net Factor Income from Abroad (NFIA): Difference between income received from other countries and paid to them.
Conclusion
National Income and Related Aggregates
These aggregates help economists understand the production and income level of a country in different ways. Remember, GDP is about the country’s territory, while National Income is about the country’s people (residents), wherever they may be. By knowing the definitions, formulas, and differences, you can easily answer any questions on national income aggregates in your class 12 Economics exam!